“A Deeper Dive into Psoriasis: Causes, Triggers, and Conventional Treatment Options”
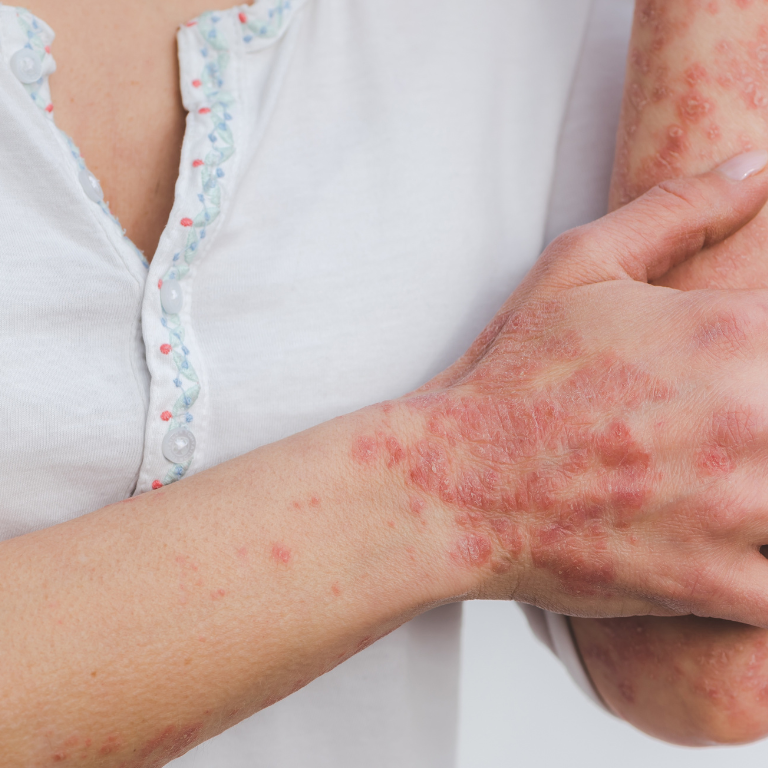
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that causes cells to build up rapidly on the surface of the skin. The extra skin cells form scales and red patches that are sometimes itchy and painful. It is a non-contagious condition, and whose exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to be related to an immune system problem.

Approximately 2-3% of the world’s population has psoriasis, which amounts to about 125 million people globally. The condition affects people of all ages and genders, although it is more common in adults and women. The incidence of psoriasis can vary from country to country. Still, it is a common condition that affects people of all races and ethnicities.
What causes Psoriasis to develop?
The exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood; however, it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Some of the factors that are thought to play a role in the development of psoriasis include:
- Genetics: Psoriasis has a strong hereditary component, and up to 10% of people with the condition have a family history of it.
- Immune system: Psoriasis is believed to be an immune-mediated condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to inflammation and the rapid production of new skin cells.
- Environmental triggers: Certain environmental triggers, such as infections (e.g., streptococcal throat infections), stress, injury to the skin (e.g., cuts, burns, or insect bites), and certain medications (e.g., beta-blockers, lithium), can cause psoriasis symptoms to worsen.
- Metabolic factors: Studies have shown that people with psoriasis have a higher risk of developing metabolic conditions, such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease, which may contribute to the development of the condition.
- Gut Imbalances – There is evidence to suggest that there is a gut-skin connection in psoriasis, meaning that imbalances in the gut microbiome can contribute to the development and severity of psoriasis – read the full bog here.
It is important to note that not everyone with these risk factors will develop psoriasis, and some people may develop the condition without any known risk factors.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
The symptoms of psoriasis can vary from person to person and may range from mild to severe.

Here are some of the most common symptoms of psoriasis:
- Red, raised patches of skin: Psoriasis typically causes red, raised patches of skin that are covered with silvery scales. These patches, also called plaques, can be itchy, painful, and may crack and bleed.
- Dry, cracked skin: The affected skin in psoriasis is often dry and can crack and bleed, especially in areas like the hands, feet, and joints.
- Itching and burning: Psoriasis can cause itching and burning sensations in the affected areas, which can be uncomfortable and disruptive.
- Nail changes:
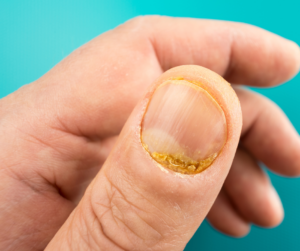 Psoriasis can cause changes to the nails, including discoloration, pitting, and thickening.
Psoriasis can cause changes to the nails, including discoloration, pitting, and thickening. - Joint pain and stiffness: In some cases, psoriasis can cause joint pain and stiffness, a condition known as psoriatic arthritis.
- Scalp psoriasis: Psoriasis can affect the scalp, causing red, scaly patches that can be itchy and flaky.
- Genital psoriasis: Psoriasis can also affect the genitals, causing red, scaly patches that can be painful and itchy.
Types of Psoriasis
There are several different types of psoriasis, each with their own distinct symptoms and characteristics. The most common types of psoriasis include:
- Plaque psoriasis: This is the most common type of psoriasis, accounting for around 80% of cases. It appears as thick, red, scaly patches on the skin that are often covered in a silver or white layer of dead skin cells. These patches can be itchy, painful, and can appear anywhere on the body.
- Guttate psoriasis: This type of psoriasis often appears after a bacterial infection, such as strep throat. It causes small, drop-shaped lesions on the skin that can appear on the arms, legs, trunk, and scalp.
- Inverse psoriasis: This type of psoriasis appears in the folds of the skin, such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts. It appears as smooth, shiny, red patches of skin that are often itchy and painful.
- Pustular psoriasis: This type of psoriasis is characterized by the appearance of pus-filled blisters on the skin. These blisters can be painful and may appear all over the body, or just on the hands and feet.
- Erythrodermic psoriasis: This is a rare and severe form of psoriasis that can be life-threatening. It causes a widespread, fiery redness of the skin, along with severe itching, swelling, and pain. People with this type of psoriasis may need hospitalization.
How to differentiate between Eczema & Psoriasis?

Eczema and psoriasis are both skin conditions that can cause red, itchy, and scaly patches; still there are several key differences between the two:
- Appearance: Eczema typically appears as red, itchy, and dry patches of skin, while psoriasis typically appears as raised, red, scaly patches with a well-defined border.
- Location: Eczema is more commonly found on the face, neck, inside of the elbows, and behind the knees, while psoriasis is more commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
- Flare-ups: Eczema often has frequent flare-ups, but the severity of symptoms can vary, while psoriasis is a chronic condition with symptoms that are more consistent and persistent.
- Scaliness: Eczema tends to have a drier, flakier appearance, while psoriasis has a more pronounced scaly appearance.
- Treatment: The treatment for eczema and psoriasis can be similar, but the specific treatment plan will depend on the severity of symptoms and the specific type of skin condition.
It is essential to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis, as the symptoms of eczema and psoriasis can sometimes overlap, and it can be challenging to differentiate between the two without a professional evaluation. A doctor can perform a physical examination, take a medical history, and possibly perform a skin biopsy to make a definitive diagnosis.
Why is Psoriasis so difficult to treat?
Psoriasis is considered a complex condition to treat because it is a chronic, recurring condition that can be influenced by several factors, including genetics, the immune system, and environmental triggers.
There is currently no cure for psoriasis, but several effective treatments are available to manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
Some of the factors that make psoriasis challenging to treat include:
- Complexity of the condition: Psoriasis is a complex condition that involves multiple systems in the body, including the skin, immune system, and genetics, making it difficult to target a single underlying cause.
- Individual variability: The severity and presentation of psoriasis can vary greatly from person to person, and what works for one person may not work for another.
- Chronicity: Psoriasis is a chronic condition that can recur even with treatment, and managing symptoms can be a lifelong process.
- Environmental triggers: Certain environmental triggers, such as stress, injury to the skin, and certain medications, can cause psoriasis symptoms to worsen, making it difficult to control.
- Resistance to treatment: Over time, the skin can become resistant to certain treatments, making it difficult to find effective options for managing symptoms.
Despite these challenges, many effective natural & conventional treatments are available for psoriasis, which I have discussed in another blog – have a look!
With the right combination of treatments and ongoing management, people with psoriasis can effectively manage their symptoms and lead a full and active life.
Connection between Psoriasis and Stress

Stress and psoriasis are interconnected in several ways. Studies have shown that stress can trigger psoriasis symptoms and make existing symptoms worse while having psoriasis can also cause stress and impact a person’s quality of life.
- Stress as a trigger: Stress can trigger the immune system, causing inflammation and leading to a flare-up of psoriasis symptoms. Stress can also make it harder for the body to fight off infections, which can also trigger psoriasis symptoms.
- Impact on quality of life: Living with psoriasis can be stressful, especially if the symptoms are severe and visible, as it can affect a person’s self-esteem, relationships, and overall quality of life.
- Stress management: Managing stress is an important part of managing psoriasis, as stress reduction can help reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms. There are several stress management techniques that can help, including yoga, exercise, mindfulness and relaxation practices, etc.
It’s important to remember that stress is just one of many factors that can impact psoriasis symptoms, and not everyone with psoriasis will experience a flare-up due to stress. Working with a doctor to develop a personalized treatment plan, incorporating stress management strategies, and seeking support from friends and family can help people with psoriasis manage their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
Conventional Treatment of Psoriasis

Currently, there is no cure for psoriasis. Still, several effective natural & conventional treatments can help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life.
The goal of conventional treatment is to reduce inflammation, slow the growth of skin cells, and relieve itching and discomfort. The specific treatment plan will depend on the severity of symptoms and the specific type of psoriasis. Some of the most common treatments for psoriasis include:
- Topical treatments: Topical creams and ointments that contain corticosteroids, vitamin D, or coal tar can help reduce inflammation and slow the growth of skin cells.
- Light therapy: Phototherapy, or light therapy, involves exposing the skin to controlled doses of natural or artificial light, which can help reduce symptoms and improve skin appearance.
- Oral or injected medications: For more severe cases of psoriasis, oral or injected medications, such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, or biologic drugs, may be necessary. These medications work by suppressing the immune system and reducing inflammation.
- Lifestyle changes: Making certain lifestyle changes, such as reducing stress, avoiding triggers, and maintaining a healthy diet, can also help improve symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
It’s crucial for individuals with psoriasis who are considering treatment options to be informed about the potential side effects of conventional treatments.
Understanding the risks and benefits of various treatment options can help individuals make informed decisions about their care and weigh the potential benefits against the potential risks.
It’s essential to have an open and honest discussion with a healthcare professional about the potential side effects of any treatment and any measures that can be taken to minimize them.
The conventional treatments for psoriasis can have a range of potential side effects. These can include:
- Topical corticosteroids: thinning of the skin, stretch marks, increased risk of infection, acne, and rosacea.
- Topical retinoids: dryness, itching, redness, and peeling of the skin.
- Phototherapy: sunburn, premature aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer.
- Systemic medications such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, and biologics: increased risk of infection, liver damage, kidney damage, blood disorders, and increased risk of certain cancers.
Psoriasis is a complex disease that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. While conventional treatments can be effective, a holistic treatment approach that addresses the underlying factors contributing to the condition can be beneficial.
This may include a combination of lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, stress reduction techniques, and complementary therapies like acupuncture and yoga. By taking a comprehensive approach to managing psoriasis, individuals may be able to improve their symptoms, reduce their reliance on medication, and achieve better overall health and well-being.
The following blog post will delve deeper into natural and holistic treatment options for psoriasis; stay tuned!
Avoiding harsh body washes and soaps can be helpful for people with psoriasis. Many conventional body washes and soaps contain harsh chemicals and fragrances that can irritate the skin and worsen psoriasis symptoms. Instead, it is recommended to use gentle, fragrance-free body washes and soaps that are specifically formulated for sensitive skin. Look for products that are free of sulfates, parabens, and other harsh chemicals, as these can be especially irritating for people with psoriasis.
Naturo Essentials Body & Hair Wash is a great option for people who are dealing with skin issues. It is Made with all-natural ingredients, it can be a good choice for people with psoriasis who are looking for a gentle, non-irritating cleanser for their skin and scalp.
Additionally, try to avoid using hot water and harsh scrubbing, as these can further dry out and irritate the skin. Instead, use lukewarm water and gentle washing motions to minimize irritation and protect the skin’s natural moisture barrier.
“Psoriasis is a complex disease which can result from a variety of contributing factors. To achieve a successful and holistic treatment outcome, I offer my support to help you identify the root cause and design a comprehensive treatment plan. This plan may encompass lifestyle modifications, topical treatments, and other natural and safe remedies with the goal of improving your skin health without any adverse side effects.” – email me at contact@naturalskin.clinic for further enquiry.
